📝 Introduction
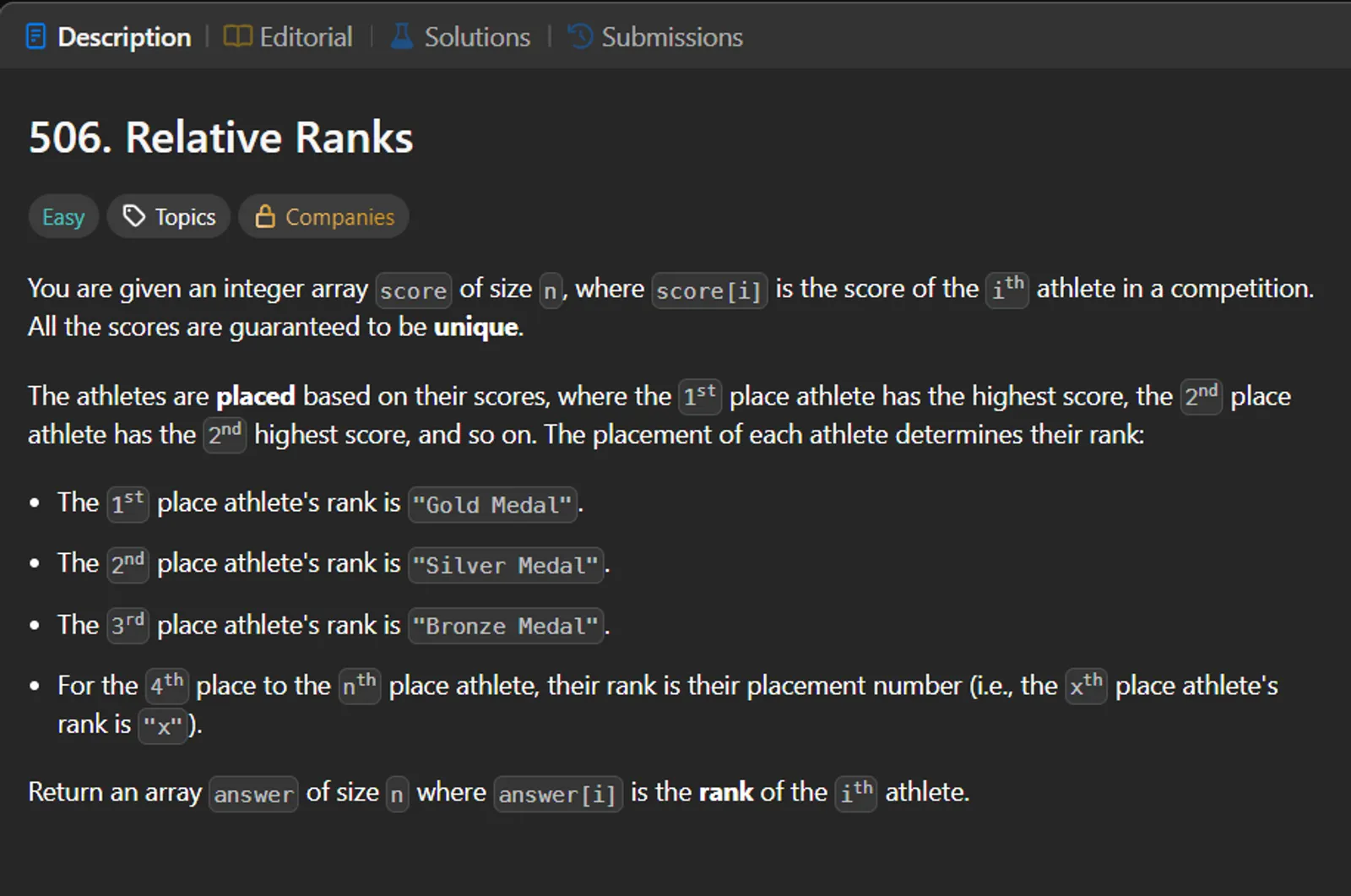
Given a list of scores representing the performance of athletes, the task is to assign ranks to them based on their scores. The top three scorers receive “Gold Medal”, “Silver Medal”, and “Bronze Medal” respectively, and the rest receive their numeric rank (starting from 4th place onward).
Constraints typically include: Each score is a unique positive integer. The output should be a list of strings corresponding to each athlete’s rank.
💡 Approach & Key Insights
The core idea is to: Track the original indices of scores. Sort the scores in descending order. Assign ranks based on sorted positions, updating the original indices accordingly. This allows easy mapping of ranks back to their original positions in the input array.
🛠️ Breakdown of Approaches
1️⃣ Brute Force / Naive Approach
- Explanation: A brute force way would be to compare each score with all others to count how many scores are higher. The rank is then one more than the number of scores higher than it. This would take O(n²) time.
- Time Complexity: O(n²) - due to nested comparisons.
- Space Complexity: O(n) - for storing result.
- Example/Dry Run:
Example input: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4]
Step 1: Count how many scores are greater for each scoreStep 2: Assign rank accordinglyStep 3: Result = ["Gold Medal", "5", "Bronze Medal", "Silver Medal", "4"]2️⃣ Optimized Approach
- Explanation: Use enumerate to pair each score with its original index. Sort the list in descending order based on score. Then iterate through the sorted list and assign ranks based on index positions.
- Time Complexity: O(n log n) – due to sorting.
- Space Complexity: O(n) – for storing result and indexed list.
- Example/Dry Run:
Example input: [10, 3, 8, 9, 4]
Step 1: indexed_scores = [(10,0), (3,1), (8,2), (9,3), (4,4)]Step 2: After sorting = [(10,0), (9,3), (8,2), (4,4), (3,1)]Step 3: Assign:
Rank 0: index 0 → "Gold Medal"Rank 1: index 3 → "Silver Medal"Rank 2: index 2 → "Bronze Medal"Rank 3: index 4 → "4"Rank 4: index 1 → "5"
Final output: ["Gold Medal", "5", "Bronze Medal", "Silver Medal", "4"]📊 Complexity Analysis
| Approach | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Brute Force | O(n²) | O(n) |
| Optimized | O(n log n) | O(n) |
📉 Optimization Ideas
The optimized solution is efficient and doesn’t need further improvement. However, using a priority queue or heap could also be considered but adds complexity without clear benefit for this problem.
📌 Example Walkthroughs & Dry Runs
Example:Input: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Process:Step 1: Pair with index → [(5,0), (4,1), (3,2), (2,3), (1,4)]Step 2: Sort by score descending → [(5,0), (4,1), (3,2), (2,3), (1,4)]Step 3: Assign ranks:0 → "Gold Medal"1 → "Silver Medal"2 → "Bronze Medal"3 → "4"4 → "5"
Output: ["Gold Medal", "Silver Medal", "Bronze Medal", "4", "5"]🔗 Additional Resources
Author: Daniel Nallapalli Date: 16/06/2025